Title: PCI-X Bus Technology – Will Connect Tech PCI boards work in my PCI-X system?
Keywords: PCI-X
Date: March 27, 2003
KDB: KDB-290
Revision: 0.00
Author: Dianna Chan
Distribution: External
Connect Tech’s products may be designed for PCI-based systems but PCI-X systems are fully backwards compatible meaning that they are able to work with previous generation PCI technology.
PCI-X was designed to deal with the increasing I/O demands of technology. PCI-X stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect Extended and it is a protocol extension of the existing PCI bus. PCI-X was developed and introduced jointly by Hewlett-Packard, IBM, and Compaq in 1998 and was submitted to the PCI Special Interest Group (PCI SIG) who then approved. Compared to the PCI, PCI-X has improved transfer rates, and increased speed and efficiency by building on the existing skills and resources of the current PCI standard, hence the name PCI-Extended.
Basic Facts On PCI-X
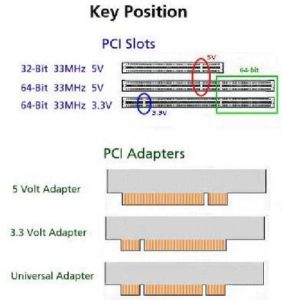
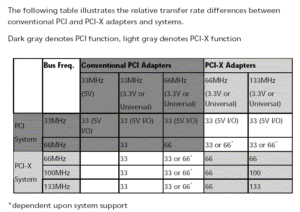
A greater bandwidth means greater amounts of data can be transferred. The 64-bit bandwidth gives PCI-X the ability to transmit 1.06 Gbit/sec, instead of 528 Mbit/sec with 32-bit PCI. This feature practically eliminates PCI data path bottlenecks. Greater I/O capacity supports the requirements for high bandwidth application such as Gigabit Ethernet, Fibre Channel, Ultra320 SCSI, Cluster Interconnects, etc. PCI-X allows for higher performance by increasing the maximum clock frequency from 66 MHz to 133 MHz. One of the most important features of PCI-X is that it is fully backwards compatible with conventional PCI products, meaning that a PCI-X adapter can be inserted into a PCI slot or conversely a PCI adapter card can be inserted into a PCI-X slot. There are no device drivers, operating system modifications, or special configuration necessary. Even though PCI-X is backwards compatible with PCI, when a PCI-X card is inserted to a PCI-based system, it will default to the speed of the PCI bus (which is 33 MHz or 66 MHz).1 Also when PCI and PCI-X cards are within the same server on a PCI-X system, the bus speed will default to the speed of the slowest card. A major benefit of this backwards compatibility is that it preserves both industry and customer investment in PCI technology.
Advanced PCI-X Features
New features added to the PCI-X are split transactions, signal timing, re-ordering of transactions, and transaction byte counts.4 Split transactions mean once a request is sent and recognized by the target, the requestor can make or receive other transactions until the target completes the first without the continual retries by the requestor (initiator) that typically occurs on the PCI bus.5 Signal timing on a PCI-X bus differs slightly from the PCI bus. On a PCI the sender drives a signal onto the bus, the signal propagates to the receiver, and the receiver decodes the signal and determines a response and the entire process happens in one clock cycle. On the PCI-X however, after sending the signal to the receiver, the signal is latched into a register and held there until the following clock cycle, giving the receiver an entire clock cycle for decoding and response determination. Even though this process adds a few clock cycles to PCI-X’s transactions, it still allows the transaction to complete much more quickly than PCI because of the higher bus frequency. The attribute phase is contained within the transaction phase of signals and it is a 36-bit attribute field that contains information about the size of the transaction, the ordering of transactions, cache snooping requirements and the transaction initiator. Current PCI-bridges can only manage transactions in the order in which they are received, but on PCI-X they use the attribute phase to re-order transactions intelligently (also known as “relaxed ordering”) to improve efficiency. This feature provides a greater advantage to delay-sensitive and time-dependent applications such as audio/video streaming.6 The transaction byte count is an improved host-to-PCI bridge that calculates an accurate byte count with each transaction in a sequence which increases the efficiency of the buffer management considerably.7 Other features which are preserved from the PCI are PCI Hot-Plug and PCI Power Management. PCI Hot-Plug is a feature which enables the user to remove, replace, or add a PCI adapter card without shutting down the server or PC. This feature is most valuable to mission-critical environments because of saving the uptime required to boot back up. PCI Power Management has a capability for the bus to be taken down to standby when it is not needed and woken at the incidence of a present external event.
Future of PCI-X Technology
In 2002, PCI-X 2.0 was introduced. PCI-X 2.0 is like a step to the next level compared to PCI-X 1.0. PCI-X 2.0 uses Double Data Rate (DDR) and Quadruple Data Rate (QDR) techniques to increase sustainable PCI bus bandwidth and now features two new speed frequencies and bandwidths: PCI-X 266 with 2.1Gbit/sec and PCI-X 533 with 4.3Gbit/sec. Like PCI-X 1.0, PCI-X 2.0 is also fully backwards compatible with past generation PCI technologies and there is no change to configurations. PCI-X 2.0 uses the same bus architecture and device drivers as all past generation PCI but also has some improvements on features such as hot-plug and power management.8 New features included on the PCI-X 2.0 are strobes, 1.5 volts signalling, ECC support, new PCI-X 2.0 registers, and higher bus efficiency. Strobes are added to ensure that the data is transferred accurately under all conditions by triggering the clock input of the data latches and ensure that signals are latched at the precise time. 1.5 volts signalling was required in order to achieve the high frequencies of PCI-X 2.0 but careful designs were made to the I/O buffers to support the 3.3 volt PCI technologies from before. ECC (Error Correcting Codes) support was added for additional fault tolerance and now it not only protects the data but also the header and it provides reliability by checking and correcting errors. In order for ECC to work, new configuration registers were created, but they also will automatically default to working values for earlier PCI technology. Higher bus efficiency is the result of addressing the criticism of previous PCI technology that overhead tasks were wasting significant bandwidth and has corrected the PCI-X protocol has been corrected to improve bus utilization.
It is said that PCI-X 1066 is in development and, it will be able to sustain as much as 8.5Gbit/sec.
Sources
1 http://searchwindowsmanageability.techtarget.com/sDefinition/0,,sid33_gci213746,00.html
2 http://www.acer.co.in/products/servers/PCI-X%20Technology%20White%20paper.pdf
3 http://www.acer.co.in/products/servers/PCI-X%20Technology%20White%20paper.pdf
4 http://www.extremetech.com/article2/0,3973,3052,00.asp
5 http://www.extremetech.com/article2/0,3973,3047,00.asp
6 http://www.acer.co.in/products/servers/PCI-X%20Technology%20White%20paper.pdf
7 http://www.qlogic.com/documents/datasheets/knowledge_data/whitepapers/tech_brief_pcix.pdf
8 http://www.serverworks.com/technology/pdf/PCI-X_2-0_WhitePaper.pdf
End of KDB-290